How to operate a drone effectively and safely is more than just pushing buttons; it’s about understanding the technology, respecting regulations, and appreciating the potential for stunning aerial photography and videography. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and ethical considerations. We’ll cover everything you need to know to confidently take to the skies with your drone.
This detailed guide will walk you through each stage of drone operation, from initial setup and safety protocols to mastering advanced flight techniques and responsible drone usage. We will explore various drone models and controllers, helping you understand their functionalities and how to use them effectively. The guide also includes troubleshooting tips and best practices for capturing breathtaking aerial images and videos.
Learn how to navigate airspace regulations and ethical considerations to ensure a safe and enjoyable experience.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring both safety and optimal performance. This involves inspecting key components, verifying environmental conditions, and understanding applicable regulations. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, equipment damage, and legal repercussions.
Pre-Flight Inspection and Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection is paramount. This involves a systematic check of various drone components, including the battery, propellers, and GPS signal. The following checklist provides a structured approach for beginners:
| Check Item | Procedure | Acceptable Result | Corrective Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Check the battery indicator on the drone and/or remote controller. | Battery level above 80%. | Charge battery if necessary. Do not fly with a low battery. |
| Propeller Condition | Visually inspect each propeller for cracks, chips, or damage. | Propellers are undamaged and securely attached. | Replace damaged propellers. |
| GPS Signal Strength | Observe the GPS indicator on the controller. | Strong and stable GPS signal (indicated by sufficient satellites). | Relocate to an area with better GPS reception if signal is weak. |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Check the gimbal for smooth movement and proper function. | Gimbal moves freely without any resistance or noise. | Check gimbal calibration or seek professional assistance if necessary. |
| Remote Controller Connection | Ensure the remote controller is properly connected to the drone. | Successful connection indicated by visual cues on the controller. | Check battery levels, power cycles the drone and remote, or check for interference. |
| Surrounding Environment | Assess the area for obstacles, people, and weather conditions. | Safe and open space, free from obstacles and hazards; suitable weather conditions. | Choose a different location if the environment is unsafe. |
Drone Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Operating a drone safely and legally requires understanding and adhering to airspace restrictions and emergency procedures. Always check local regulations and obtain necessary permits before flying. Familiarize yourself with no-fly zones, such as airports, stadiums, and restricted areas. In case of emergencies, practice controlled descents and have a plan for retrieving your drone safely.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Effective drone operation hinges on understanding and mastering the drone’s controls and navigation systems. Different controllers offer varying functionalities, impacting the ease and precision of flight. Furthermore, understanding basic flight controls allows for precise maneuvering.
Types of Drone Controllers
Several types of drone controllers exist, each with its own set of features and functionalities. Three common types include:
- Standard Gamepad-Style Controllers: These controllers mimic the layout of a video game controller, offering intuitive control over the drone’s movements. They typically feature joysticks for directional control and buttons for various functions.
- Modular Controllers: These controllers allow for customization and expansion through the addition of modules or accessories. This adaptability makes them suitable for a wider range of applications and allows for personalized control configurations.
- Smartphone/Tablet Controllers: These controllers use a smartphone or tablet as the primary interface, providing a touchscreen-based control system. This option is often more portable and can offer advanced features through dedicated apps.
Basic Flight Controls
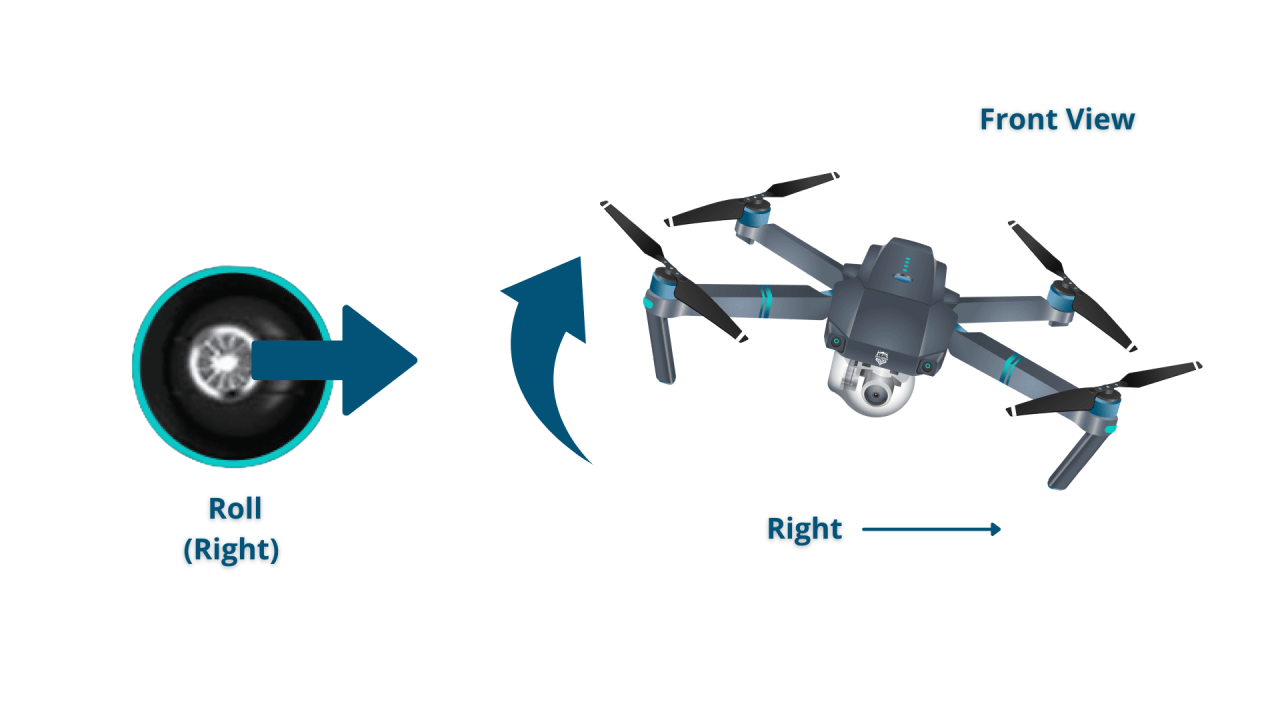
Understanding the four basic flight controls is essential for safe and controlled flight:
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s altitude; increasing throttle causes the drone to ascend, decreasing it causes descent.
- Pitch: Controls movement forward and backward; tilting the control stick forward moves the drone forward, tilting it backward moves it backward.
- Roll: Controls movement left and right; tilting the control stick to the left moves the drone to the left, tilting it to the right moves it to the right.
- Yaw: Controls the drone’s rotation; rotating the control stick left or right causes the drone to turn in the corresponding direction.
Simple Flight Training Exercise
Beginners should start with a simple flight training exercise in a safe, open area. The following steps are recommended:
- Hovering Practice: Practice maintaining a stable hover at a low altitude. Focus on smoothly adjusting the throttle to counteract any drift.
- Forward/Backward Flight: Practice smooth forward and backward movements, keeping the drone at a consistent altitude. Gradually increase the distance of these movements.
- Side-to-Side Flight: Practice smooth side-to-side movements, again maintaining a consistent altitude. Gradually increase the distance of these movements.
- Turning Practice: Practice smooth turns, focusing on controlled yaw movements. Avoid sharp turns, especially at higher altitudes.
Taking Off, Landing, and Basic Maneuvers
The procedures for taking off and landing a drone, along with executing basic maneuvers, are fundamental to safe and effective drone operation. Different environments may require adjustments to these procedures to account for potential hazards.
Taking Off and Landing Procedures
For takeoff, begin by ensuring the drone is in a safe, open area away from obstacles. Power on the drone and controller, wait for the GPS signal to lock, and then initiate a slow, controlled ascent. For landing, initiate a slow, controlled descent, maintaining visual contact with the drone. Land gently in a designated area.
Tips for Smooth Ascents and Descents

Smooth ascents and descents are essential for preventing sudden movements that can lead to accidents or damage. Use gentle, controlled inputs on the throttle, avoiding sudden jerks or rapid changes in altitude. Maintain visual contact with the drone throughout the entire process.
Basic Maneuvers
Basic maneuvers such as hovering, forward/backward flight, side-to-side flight, and turning are crucial for effective drone control. Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area, gradually increasing the complexity and distance of your movements. Always prioritize safety and controlled movements to prevent accidents.
Advanced Flight Techniques and Features
Advanced flight modes and features enhance drone operation, providing increased safety and control. These features are particularly beneficial for complex maneuvers and challenging environments. Understanding these features allows for more creative and efficient drone use.
Advanced Flight Modes
Many drones offer advanced flight modes such as GPS mode, altitude hold, and return-to-home (RTH). GPS mode utilizes satellite signals for precise positioning, altitude hold maintains a constant altitude, and RTH automatically returns the drone to its starting point. These features significantly improve safety and simplify operation, especially for beginners.
Waypoints and Pre-programmed Flight Paths
Waypoints allow you to pre-program a flight path for your drone, enabling automated flights along a defined route. This is useful for tasks like aerial photography or surveying. Pre-programmed flight paths eliminate the need for constant manual control, freeing up the operator to focus on other tasks such as camera operation.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace. Mastering the art of drone operation takes practice, but with the right guidance, you’ll be soaring in no time.
Remember to always prioritize safety when operating a drone.
Camera Controls
Modern drones typically incorporate high-quality cameras. Understanding camera controls, including zoom, focus, and image/video recording, is crucial for capturing high-quality aerial footage. Most drones allow for these adjustments through the controller or a dedicated mobile application.
Drone Photography and Videography: How To Operate A Drone

Capturing stunning aerial footage requires understanding proper camera settings, composition techniques, and best practices. This section explores techniques for creating compelling visual content with your drone.
Camera Settings for Optimal Image and Video Quality
Proper camera settings are critical for achieving optimal image and video quality. Experiment with different settings, such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture, to find the best combination for various lighting conditions. Higher resolutions generally result in better quality but require more storage space.
Tips for Composing Compelling Aerial Shots and Videos
Composing compelling aerial shots involves careful consideration of framing, perspective, and the overall visual narrative. Use the drone’s ability to move smoothly and dynamically to create visually interesting shots. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to find the most captivating viewpoints.
Best Practices for Capturing Stunning Aerial Footage
Several best practices enhance the quality of aerial footage. These include:
- Lighting: Shoot during the “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) for optimal lighting conditions.
- Composition: Use the rule of thirds to create balanced and visually appealing compositions.
- Flight Path: Plan your flight path carefully to ensure smooth transitions and avoid jerky movements.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is vital for extending the lifespan of your drone and preventing malfunctions. This involves a routine cleaning, battery care, and propeller checks. Understanding common issues and troubleshooting steps is equally important for maintaining operational readiness.
Regular Drone Maintenance
A regular maintenance schedule ensures optimal drone performance. This includes:
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the drone body, propellers, and camera lens to remove dirt and debris.
- Battery Care: Store batteries in a cool, dry place and avoid overcharging or deep discharging them.
- Propeller Inspection: Regularly inspect propellers for cracks, chips, or damage and replace them as needed.
- Firmware Updates: Keep the drone’s firmware updated to benefit from bug fixes and new features.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Their Causes, How to operate a drone
Common drone malfunctions include low battery, GPS signal loss, and motor problems. Low battery is often due to extended flight time or old batteries. GPS signal loss can result from poor signal strength or interference. Motor problems might be caused by debris or damage.
Troubleshooting Steps for Common Issues
Troubleshooting steps vary depending on the specific issue. For low battery, charge the battery or replace it with a fully charged one. For GPS signal loss, relocate to an area with better reception. For motor problems, inspect the motors for debris or damage and seek professional repair if needed.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Drone operation is subject to various legal and ethical considerations. Understanding and adhering to these guidelines ensures responsible and legal drone usage.
Relevant Laws and Regulations
Before operating a drone, research and understand all applicable local, state, and federal laws and regulations. These regulations often cover airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limitations. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines or legal action.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are paramount in drone operation. These include respecting privacy, avoiding intrusive surveillance, and being mindful of the impact on the environment and wildlife. Responsible flying practices ensure that drone usage is ethical and does not negatively impact others.
Ethical Dilemma Scenario and Solution
Imagine a scenario where a drone operator discovers illegal activity while filming. The ethical dilemma involves whether to report the activity, potentially jeopardizing their own privacy or legal standing. A possible solution involves anonymously reporting the activity to the appropriate authorities, ensuring the safety and well-being of those involved.
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding journey that blends technology, skill, and responsibility. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can confidently navigate the skies, capture stunning visuals, and adhere to safety and ethical guidelines. Remember that consistent practice, adherence to regulations, and a respect for airspace will make your drone flying experience both safe and enjoyable. Embrace the possibilities, but always prioritize safety and responsible operation.
FAQ Corner
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functions. Look for models with straightforward controls and good online support.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your drone’s compass before each flight is recommended, especially if you’re in an area with significant magnetic interference. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
What is the legal range for flying a drone?
Legal drone flight ranges vary by location and regulations. Always check local laws and FAA (or equivalent) regulations before flying. Many jurisdictions limit range and require registration.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic flight maneuvers. Learning to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced techniques. With practice and a solid understanding of the fundamentals, you’ll be confidently operating your drone in no time.
If you lose control, immediately engage the “Return to Home” (RTH) function if available. If RTH fails, try to land it manually. If neither is possible, contact local authorities to report the lost drone.
